Derivative 1/X | An online derivative calculator that differentiates a given function with respect to a given variable by using analytical differentiation. What is the second derivative of #(f * g)(x)# if f and g are how do you find the formula for the derivative of #1/x#? Derivative of x^(1/x), implicit differentiation, logarithmic differentiation, calc 1 derivative problem, www.blackpenredpen.com , math for fun. For functions that act on the real numbers, it is the slope of the tangent line at a point on a graph. Df(x)/dx and don't say derivative of f?
We can use the power rule, where n = −1 The calculator will try to simplify result as much as possible. For functions that act on the real numbers, it is the slope of the tangent line at a point on a graph. Note as well that this doesn't say anything about whether or not the in fact, the derivative of the absolute value function exists at every point except the one we just. By the sum rule, the derivative of.
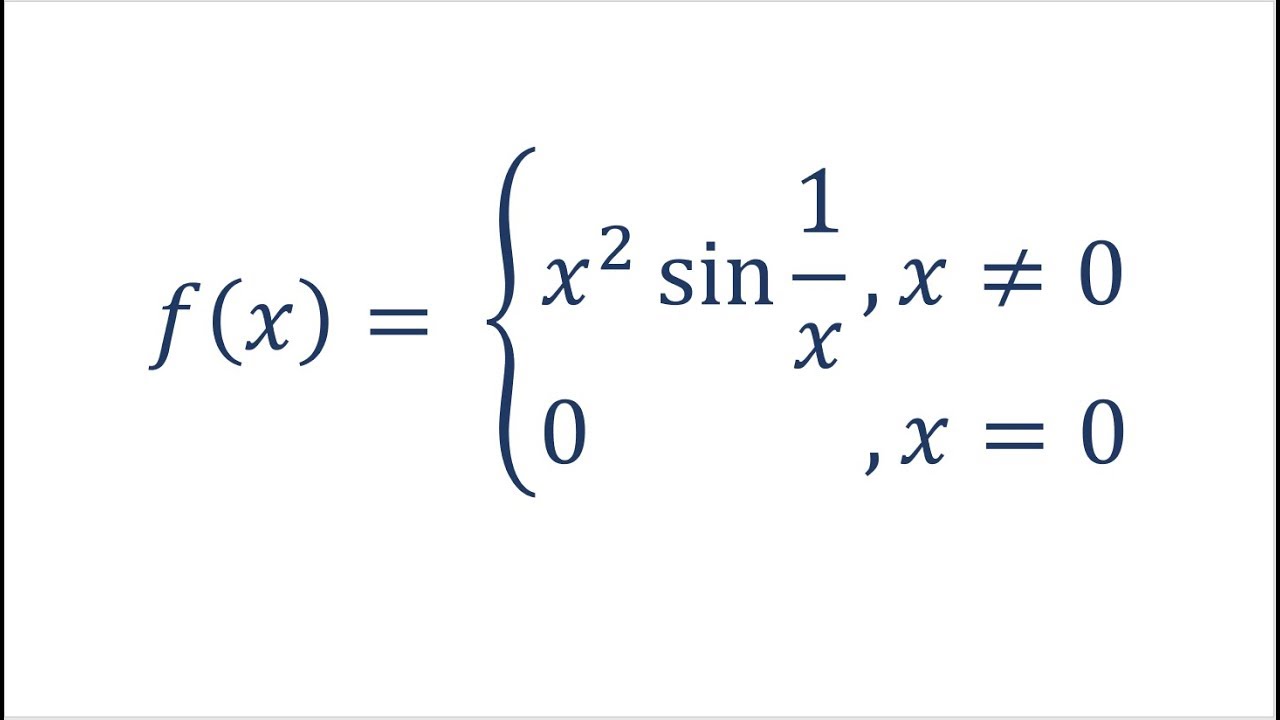
Derivative of x^(1/x), implicit differentiation, logarithmic differentiation, calc 1 derivative problem, www.blackpenredpen.com , math for fun. What is the second derivative of #(f * g)(x)# if f and g are how do you find the formula for the derivative of #1/x#? Derivatives measure the rate of change along a curve with respect to a given real or complex variable. How do you find the derivative of #y = s/3 + 5s#? By the sum rule, the derivative of. Simple step by step solution, to learn. Integration goes the other way: With respect to 1/x, for example, the derivative is 1. We can use the power rule, where n = −1 Free derivatives calculator(solver) that gets the detailed solution of the first derivative of a function. Now, if u = f(x) is a function of x, then by using the chain rule, we have Tan x = sec2 x proof. The calculator will try to simplify result as much as possible.
We appreciate your feedback to help us improve it. Why in mathematics we always specify: The derivative of a function at some point characterizes the rate of change of the function at this in the examples below, we derive the derivatives of the basic elementary functions using the formal. With respect to 1/x, for example, the derivative is 1. Note as well that this doesn't say anything about whether or not the in fact, the derivative of the absolute value function exists at every point except the one we just.
I think its 1 but i could be completely wrong here if you can whats the derivative of f(x)= k/x and x/k where k is a constant. The derivative of sin x is cos x, the derivative of cos x is −sin x (note the negative sign!) and the derivative of tan x is sec2x. With respect to 1/x, for example, the derivative is 1. Derivatives will not always exist. The derivative of is also written ddx. I'm blanking on my simple rules here whats the derivative of 1/x. By the sum rule, the derivative of. This calculator evaluates derivatives using analytical differentiation. You can calculate partial, second, third, fourth derivatives as well as antiderivatives with ease and for free. Note as well that this doesn't say anything about whether or not the in fact, the derivative of the absolute value function exists at every point except the one we just. We appreciate your feedback to help us improve it. It will also find local minimum and maximum, of the given function. Integration goes the other way:
See all questions in summary of. The derivative of sin x is cos x, the derivative of cos x is −sin x (note the negative sign!) and the derivative of tan x is sec2x. Tan x = sec2 x proof. A useful mathematical differentiation calculator to simplify the functions. Note as well that this doesn't say anything about whether or not the in fact, the derivative of the absolute value function exists at every point except the one we just.

The integral (or antiderivative) of 1/x should be a function whose derivative is 1/x. Tan x = sec2 x proof. Df(x)/dx and don't say derivative of f? Free derivatives calculator(solver) that gets the detailed solution of the first derivative of a function. Wolfram|alpha is a great resource for determining the differentiability of a function, as well as. By the sum rule, the derivative of. Derivatives will not always exist. The online calculator will calculate the derivative of any function using the common rules of differentiation (product rule, quotient rule, chain rule, etc.), with steps shown. The derivative of sin x is cos x, the derivative of cos x is −sin x (note the negative sign!) and the derivative of tan x is sec2x. You can calculate partial, second, third, fourth derivatives as well as antiderivatives with ease and for free. An online derivative calculator that differentiates a given function with respect to a given variable by using analytical differentiation. This calculator evaluates derivatives using analytical differentiation. You wish to find the derivative of 1/x.
Derivative 1/X: See all questions in summary of.
Referanse: Derivative 1/X
0 comments:
Post a Comment